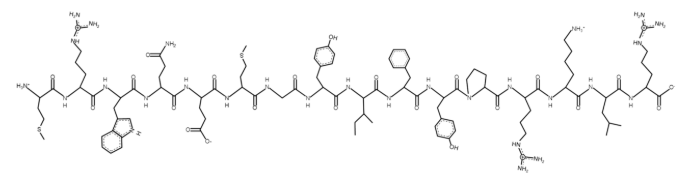
Sequence: Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg
Molecular Formula: C101H152N28O22S2
Molecular Weight: 2174.64 g/mol
PubChem SID: 255386757
CAS Number: 1627580-64-6
Synonyms: Mitochondrial open reading frame of the 12S rRNA-c, MT-RNR1
Research in mice indicates the MOTS-c can reverse age-dependent insulin resistance in muscles, thereby improving muscle uptake of glucose. It does this by improving skeletal muscle response to AMPK activation, which in turn increases the expression of glucose transporters[1]. It is important to note that this activation is independent of the insulin pathway and thus offers an alternative means of boosting glucose uptake by muscles when insulin is ineffective or in insufficient quantity. The net result is improved muscle function, enhanced muscle growth, and decreased functional insulin resistance.
Research in mice has shown that low levels of estrogen lead to increased fat mass and dysfunction of normal adipose tissue. This scenario increases the risk of developing insulin resistance and, subsequently, the risk of developing diabetes. Supplementing mice with MOTS-c, however, increases brown fat function and reduces the accumulation of adipose tissue. It also appears that the peptide prevents adipose dysfunction and the adipose inflammation that typically precedes insulin resistance[2].
It appears that at least part of the influence that MOTS-c has on fat metabolism is mediated through activation of the AMPK pathway. This well-defined pathway is turned on when cellular energy levels are low and it drives the uptake of both glucose and fatty acids by cells for metabolism. It is also the pathway that is activated in ketogenic diets, like the Atkin’s diet, which promote fat metabolism while protecting lean body mass. MOTS-c targets the methionine-folate cycle, increases AICAR levels, and activates AMPK.
New research suggests that MOTS-c can actually leave the mitochondria and make its way to the nucleus where the peptide can affect nuclear gene expression. Following metabolic stress, MOTS-c has been shown to regulate nuclear genes involved in glucose restriction and antioxidant responses[3].
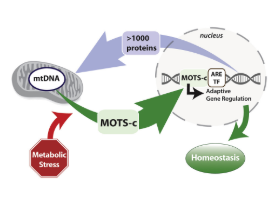
MOTS-c has effects in both the mitochondria and the nucleus.
Source: Cell Metabolism
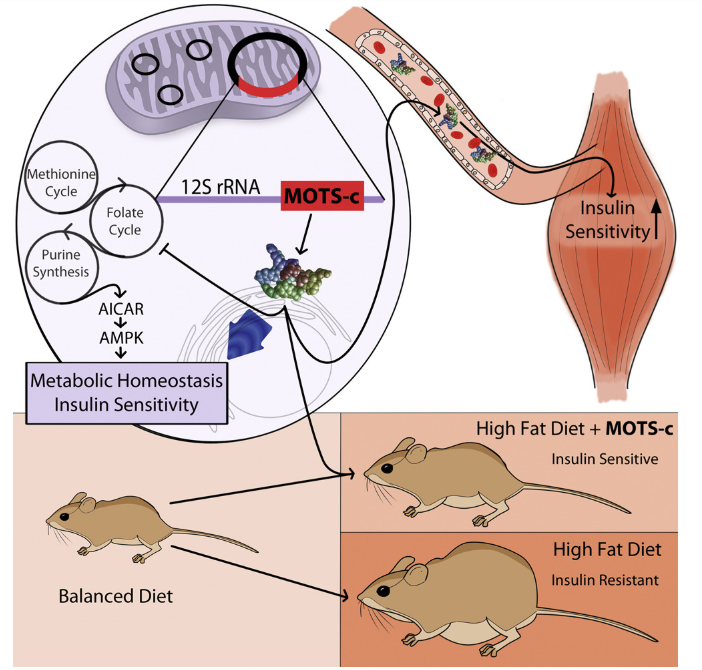
MOTS-c supplementation in rats prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and prevents the accumulation of fat even in the setting of a high-fat diet.
Source: Cell Metabolism
Research measuring MOTS-c levels in insulin sensitive and insulin resistant individuals has shown that the protein is associated with insulin sensitivity only in lean individuals. In other words, MOTS-c appears to be important in the pathogenesis of insulin insensitivity, but not in the maintenance of the condition[6]. Scientists speculate that the peptide maybe a useful means of monitoring pre-diabetic lean individuals and that changes in MOTS-c levels could act as an early warning sign of potential insulin insensitivity. Supplementation with MOTS-c in this setting could help to stave off insulin resistance and thus the development of diabetes. Research in mice thus far has been promising, but more work is needed to understand the full impact of MOTS-c on insulin regulation.